In the vast landscape of online commerce, choosing the right e-commerce model can significantly impact your business’s success and growth. Having navigated various e-commerce models myself, I’ve gathered insights and experiences that can help you understand the different approaches and decide which one best aligns with your goals. Join me as we explore the diverse e-commerce models available today.
Understanding E-commerce Models

E-commerce models define how businesses sell products or services online, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and challenges. Understanding these models is essential for long-term success, whether you’re just starting or looking to optimize your current strategy.
1. Business-to-Consumer (B2C) E-commerce
Overview: B2C is the most common e-commerce model where businesses sell directly to consumers.
Characteristics:
- Direct Sales: Products are marketed and sold directly to end-users.
- Wide Audience Reach: Targeting a broad consumer base through digital marketing channels.
- Customer-Centric: Focus on creating a seamless shopping experience and building customer relationships.
Benefits:
- Scalability: Potential to reach a large audience globally.
- Direct Feedback: Direct interaction with customers for feedback and insights.
- Flexibility: Ability to adjust pricing and promotions quickly.
Challenges:
- Competition: High competition in popular consumer markets.
- Customer Acquisition: Acquiring and retaining customers in a crowded marketplace is costly.
- Logistics: Efficient logistics management is crucial for timely deliveries.
2. Business-to-Business (B2B) E-commerce
Overview: B2B e-commerce involves transactions between businesses, such as manufacturers selling to wholesalers or retailers.
Characteristics:
- Bulk Orders: Typically involves larger order quantities.
- Relationship-Focused: Building long-term relationships with business customers.
- Customized Pricing: Negotiated pricing based on order volumes and terms.
Benefits:
- Higher Order Values: Larger and more consistent order sizes.
- Relationship Building: Opportunities for repeat business and loyalty.
- Streamlined Processes: Automation of procurement and inventory management.
Challenges:
- Complex Sales Cycles: Longer decision-making processes.
- Customization: Meeting specific business requirements and customization demands.
- Market Saturation: Competitive landscape with established B2B players.
3. Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) E-commerce
Overview: C2C e-commerce facilitates transactions between individual consumers through online platforms.
Characteristics:
- Peer-to-Peer Sales: Individuals sell directly to other consumers.
- Marketplace Platforms: Platforms act as intermediaries (e.g., eBay, Etsy).
- Product Variety: Wide range of products and services sold by individuals.
Benefits:
- Accessibility: Anyone can sell products without a formal business setup.
- Cost-Effective: Lower overhead costs compared to traditional retail models.
- Diverse Inventory: Access to unique and niche products.
Challenges:
- Trust and Security: Ensuring trust between buyers and sellers.
- Quality Control: Managing product quality and customer expectations.
- Transaction Fees: Platform fees can impact sellers’ profitability.
4. Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) E-commerce
Overview: D2C e-commerce bypasses traditional retail channels, allowing brands to sell directly to consumers.
Characteristics:
- Brand Control: Brands maintain control over the entire customer experience.
- Data Ownership: Access to valuable customer data and insights.
- Marketing Agility: Ability to tailor marketing strategies and messaging directly to consumers.
Benefits:
- Brand Loyalty: Direct engagement fosters stronger brand-consumer relationships.
- Higher Margins: Cutting out intermediaries increases profit margins.
- Market Testing: Rapid testing and iteration of products and marketing strategies.
Challenges:
- Distribution: Establishing efficient logistics and fulfillment capabilities.
- Customer Acquisition: Building brand awareness and acquiring new customers.
- Scale: Scaling operations while maintaining product quality and customer satisfaction.
Choosing the Right E-commerce Model for Your Business
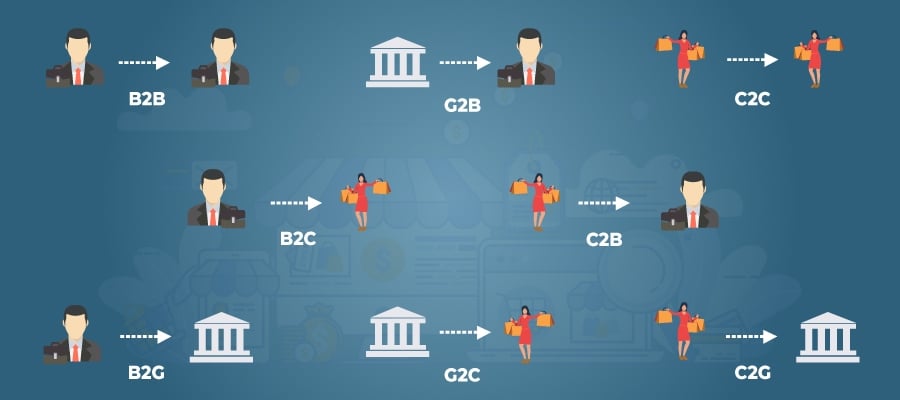
Factors to Consider:
- Target Audience: Understanding your customer demographics and buying behavior.
- Product Characteristics: Complexity, price point, and market demand.
- Competitive Landscape: Assessing competition and market saturation.
- Business Goals: Short-term revenue goals and long-term growth strategy.
Personal Insights: In my e-commerce journey, I initially focused on a B2C model due to its scalability and direct customer interaction. As my business evolved, integrating elements of D2C allowed me to build a more substantial brand presence and control over customer relationships. Understanding these models helped me adapt strategies and optimize operations for sustained growth.
Navigating E-commerce Models
Choosing the suitable e-commerce model is a pivotal decision that shapes your business strategy, customer relationships, and operational efficiency. Whether you opt for B2C, B2B, C2C, or D2C, each model offers unique opportunities and challenges. You can create a sustainable and successful online venture by aligning your choice with your business objectives and customer needs. Here’s to navigating the diverse e-commerce landscape and unlocking your business’s full potential.



